In a very short period, health care systems and society have been severely challenged by yet another emerging virus. Preventing transmission and slowing the rate of new infections are the primary goals; however, the concern of COVID-19 causing critical illness and death is at the core of public anxiety.
Laboratory tests are more crucial than ever in clinical decision making for these critically ill patients that have either conjoint morbidities or have developed other acute conditions based on the COVID-19 infection.
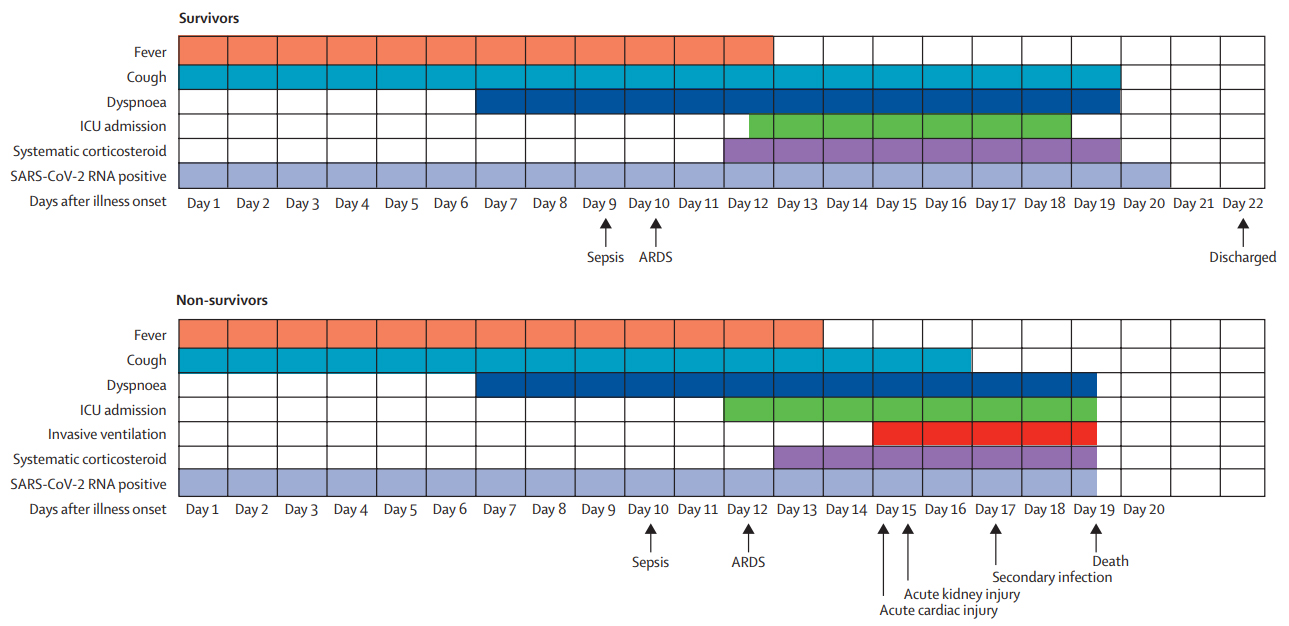
It has been observed that the clinical course of adult inpatients may include sepsis, acute cardiac injury or acute kidney injury among others (1). The following graphic, from Elsevier Ltd., shows the moment of the COVID-19 infection evolution in which these complications appear for survivor and non-survivor patients (1):
Biochemical monitoring of COVID-19 patients through in vitro diagnostic testing is critical for assessing disease severity and progression as well as monitoring therapeutic intervention.
- Laboratory abnormalities in patients with COVID-19:
https://www.med.uminho.pt/pt/covid19/Progresso%20da%20Doena/Lippi-2020-Laboratory%20abnormalities%20in%20patient.pdf - Biochemical Monitoring of COVID-19 Patients:
https://www.ifcc.org/ifcc-news/2020-03-26-ifcc-information-guide-on-covid-19/
Ortho provides hospital labs with instruments, assays and services that enable the quickest and most accurate delivery of test results to meet patient needs and expectations when treating life threatening situations.
Learn more about how we support the laboratories to deliver the right result the first time:
- About Ortho
Brochure
- Acute Kidney Injury Complications – Renal Biomarker*
VITROS® NEPHROCHECK® Brochure
- Cardiac Complications – Biomarkers**
VITROS® hsTroponin I Brochure*, D-Dimer Brochure, VITROS® NT-proBNP Brochure, VITROS® NT-proBNP Brochure (US only)
- Sepsis Management – PCT Biomarker**
VITROS® B•R•A•H•M•S PCT Brochure, VITROS® B•R•A•H•M•S PCT Sell sheet (US only)
- The importance of assay Interferences in getting the right result the first time during times of crisis
Visit our landing page
- Integrity driven testing process in the aid of results availability
VITROS® XT Solutions Brochure, VITROS XT Total Lab Solutions (US)
- Broader Assay Menu
VITROS® Assay Menu Brochure
References:
- Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Zhou et al, www.thelancet.com. Published online March 9, 2020 https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3. Accessed on 25th April 2020.
- https://www.ifcc.org/ifcc-news/2020-03-26-ifcc-information-guide-on-covid-19/. Accessed on 12th May 2020
*Not available is US
**Not all products are available for sale in all countries.
Press contact:
For media inquiries please contact
Ortho Media Relations
Ortho Clinical Diagnostics
media@quidelortho.com
.jpg)
